Comparison of sorting algoritms
August 9, 2012Searching in a linked list
August 10, 2012How to delete a node in a linked list if only pointer to node is given?
Given a pointer to Node in a Singly linked list. Is it possible to delete the same node ?
The procedure to delete a node in a Singly linked list requires a pointer to the previous Node. Suppose we want to delete Node with value 5 from the below linked list. Then we need to pointer to the previous Node (4). ptr may not be given, but prev is required.
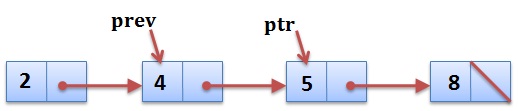
// ptr will point to the Node to be deleted.
// Need this pointer because we need to free(delete) the memory allocated to it.
Node* ptr = prev->link;
// Removing Node (ptr) from the linked list
prev->link = ptr->link;
// Deallocating memory allocated to ptr
delete ptr;
According to the question, we does not have a pointer to the previous Node. Only ptr is given to us. Can we now delete the Node 5.
The Answer is both Yes & No.
There is a Not-So-Clean way to delete the Node.
1. Copy data of the Node next to ptr to Node pointed to by ptr. 2. Remove the Next Node.
Code:
// Copying data of next Node to ptr
ptr->data = ptr->link->data;
// We can now delete the next node and keep ptr.
Node* temp = ptr->link;
// Removing Node 'temp' from the linked list
ptr->link = temp->link;
// Deallocating memory allocated to temp
delete temp;
But there is a flaw in the above code. What if ptr is pointing to the last Node of the list? Then there is no way to delete the Node.
The Structure of Node used for this program is
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* link;
};
Note: If pointer to the head (start of List) is given, then we can traverse to the parent of the Node and delete the Node. In this question we have dealt with the case when No other pointer to List is given except for pointer to the node to be deleted.
What if it is a doubly linked list ?
In doubly linked list, every node has a pointer to the previous node also (in addition to a pointer to the next Node). Structure of node is
struct
{
int data;
Node* previous;
Node* next;
};
Hence, it is not a problem to get a pointer to the previous Node. Just that pointers need to be manipulated more because there are two pointers per Node.
Node* prev = ptr->previous;
// Removing Node (ptr) from the linked list
prev->next = ptr->next;
ptr->next->previous = prev;
// Deallocating memory allocated to ptr
delete ptr;
