Speed and time question
August 22, 2012Check if a Binary Tree is Binary Search Tree
August 23, 2012Convert a Binary Tree to Binary Search Tree
Given a Binary Tree, write code to convert it to Binary Search Tree such that the structure of the tree remains the same. For example: Both the below trees
5 10
/ \ / \
8 10 5 30
/ \ \ / \ \
4 30 1 8 40 1
/ /
40 4
Should generate the below Binary Search Tree.
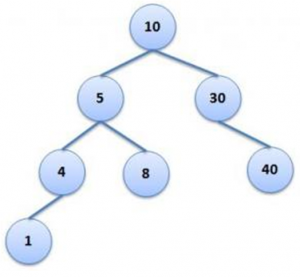
Note that the structure of the tree remains the same. Hence all the three trees above are Similar.
Solution:
For this we need an extra array of size n (Number of Nodes) to store the inorder traversal of the tree.
Algorithm:
1. Traverse the tree in inorder and store the values in array. 2. Sort the Array. 3. Traverse the tree again in in-order and copy the values from array in the Nodes.
Code:
/**
* Populate the array arr with the inorder traversal of the tree pointed to by r.
* pos holds a reference to the current poisition of arr.
*/
void populateInorderArray(Node* r, int* arr, int* pos)
{
if(r == NULL)
return;
populateInorderArray(r->lptr, arr, pos);
arr[*pos] = r->data;
(*pos)++;
populateInorderArray(r->rptr, arr, pos);
}
/**
* Traverse the Tree in Inorder traversal and copy the values from
* array arr to the nodes of the tree.
*
* pos holds a reference to the current poisition of arr.
*/
void copyInorderArrayToTree(Node* r, int* arr, int* pos)
{
if(r == NULL)
return;
copyInorderArrayToTree(r->lptr, arr, pos);
r->data = arr[*pos];
(*pos)++;
copyInorderArrayToTree(r->rptr, arr, pos);
}
/** Functions accepts a pointer to the root of a Binary Tree
* and converts it to Binary Search Tree.
* We don't need a Node**, because we are not changing the root node,
* We are only changing the value contained in the root node.
*
* Structure of the tree remains the same.
*/
void converttoBST(Node* r)
{
if(NULL == r)
return;
// hard-codding it to 1000 for simplicity.
// define the array equal to number of nodes.
int arr[1000] = {0};
int n = 0; // Will hold the number of Nodes
populateInorderArray(r, arr, &n);
quickSort(arr, 0, n-1);
n=0;
copyInorderArrayToTree(r, arr, &n);
}
I am sure you can write the Quick Sort algorithm. Ok, let me write the function to sort the array also (as used in the above code).
/** Helper function to partition the array for a pivot.
*/
int partition(int *arr, int low, int high)
{
int p = low;
low++;
while(low<=high)
{
while(arr[low]<arr[p]) low++;
while(arr[high]>arr[p]) high--;
if(low<high)
{
int temp = arr[low];
arr[low] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
}
}
int temp = arr[p];
arr[p] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return high;
}
/** Function to sort the array using Quick sort algorithm
*/
void quickSort(int* arr, int a, int b)
{
if(a>=b)
return;
int pos = partition(arr, a, b);
quickSort(arr, a, pos-1);
quickSort(arr, pos+1, b);
}
Time Complexity:
Time to populate Inorder Array = O(n)
Time to Sort Inorder Array = O(n.lg(n))
Time to Put values from Sorter array to Tree = O(n)
Total Time = O(n) + O(n.lg(n)) + O(n) = O(n.lg(n))
Note: The above implementation of Quick sort takes O(n2) time in worst case, because we are not choosing the pivot randomly. But a randomized Quick Sort algorithm takes O(n.lg(n)) time in the worst case.
Extra Space Used: O(n)
Note: The array uses extra space O(n). even if we do not use the array, the Inorder algorithm takes O(n) space because of Recursion.

1 Comment
hi this is my function which converts the sorted array to BST
public static void BTtoBSTUtil2(Node root,ArrayListarr,int i) {
System.out.println(“i1″+i);
if(root!=null) {
BTtoBSTUtil2(root.left, arr,i);
// System.out.println(“i1″+i);
root.data=arr.get(i);
i++;
//System.out.println(“i2″+i);
BTtoBSTUtil2(root.right, arr,i);
}
}
Its not working. Please help me out